COURSES
We offer a diverse range of courses, from beginner to advanced levels, tailored to fit your learning needs. Designed to be modular, these courses allow you to learn at your own pace and focus on topics that align with your goals.
Introduction to Industrial Knit
IIK001B

Level: Beginner
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
Get a first look at the field of industrial knitting in Introduction to Industrial Knit. This short course unpacks the technology, techniques, and possibilities of modern knit manufacturing, offering a glimpse into its creative and technical potential.
Introduction to Yarn
IY002B

Level: Beginner
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
Gain a foundational understanding of yarn and its role in industrial knitting. This course explores fibre types, yarn structures, and their impact on performance, helping you make informed choices for design and production.
Understanding Knit Machinery
UKM005B
Level: Beginner
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
Explore the essential machines used in knit production, from linkers and cup seamers to the components of industrial knitting machines. Learn about different flatbed machine types, their capabilities, and how they impact design and manufacturing efficiency. Suitable for those looking to deepen their technical knowledge of knit production.
Knit Production Basics
KPB004B
Level: Intermediate
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
Gain an introductory understanding of the knitwear production process, from development to final product. This course covers key factors like manufacturing considerations, quality assurance, and costing. Learn how to navigate production efficiently while balancing design integrity, budget, and sustainability.
Exploring 3D Knitting: How to Rethink Knit

Level: Beginner
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
Explore how 3D knitting is shaping both fashion and industrial design. Learn about real-world applications, from seamless garments to technical textiles, and discover the innovative approaches used by contemporary designers and developers. Gain an understanding of how this technology pushes the boundaries of sustainability, efficiency, and design possibilities across industries.
Designing with Jacquards

Level: Intermediate
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
This course introduces the possibilities of jacquard knitting in this course, covering the techniques, limitations, and creative potential of machine-knitted jacquards. Learn how to design patterns, optimise for production, and effectively communicate with suppliers to achieve the best results. Perfect for designers looking to harness the full potential of jacquard technology in fashion and beyond.
Methods of Garment Construction

Level: Beginner
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
This mini-course breaks down key construction methods in industrial knitting: cut and sew, fully fashioned, and complete knitting. Learn how each approach affects design, production, and sustainability, including material efficiency, waste reduction, and manufacturing constraints. Ideal for designers looking to make informed decisions about structure, aesthetics, and responsible production.
Stitch Structures

Level: Beginner
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
Unpack different industrial knit stitch structures, from plain and purl to ribs, textured stitches, tuck, transfer, links-links, and colourwork techniques like intarsia and jacquard. This course explores how stitch selection impacts design, functionality, and production, helping you make informed choices for your knit projects.
Design your First Jumper

Level: Beginner
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
Learn the fundamentals of designing a jumper in this beginner-friendly online course. Whether you're new to knitwear design or looking to refine your approach, this course will guide you through the essential steps from concept development and yarn selection to basic pattern creation and construction techniques.
Introduction to Tech Packs

Level: Beginner
Duration: 1 hour
Duration: 1 hour
Get an overview of the key components required in a knitwear tech pack, including structure maps, swatch references, measurement guides, and labeling details. Understand how these elements come together to ensure clear communication with manufacturers and a smooth production process.
Foundations of Industrial Knit

Level: Beginner
Duration: 6 hours
Duration: 6 hours
Build a solid understanding of industrial knitting in Foundations of Industrial Knit. This course breaks down key techniques, machinery, and processes, giving you the knowledge to translate design concepts into production-ready knitted products. This course provides you with the tools to navigate this advanced manufacturing landscape with confidence.
Testimonials
"Woolmark have had the pleasure of onboarding Patricia as an education consultant for a number of advanced knitwear presentations within our Merino wool retailer training programs, and I can confidently say she is an exceptional knitwear expert. Her deep knowledge of advanced knitwear design and construction, combined with her clear and engaging presentation style, is warmly received by each attendee of her workshops. She effortlessly demonstrated her expertise in both the technical aspects of seamless knitting and its creative possibilities, offering valuable insights that resonated with each of the workshop participants.
Patricia is not only highly skilled but also passionate about her work, and I recommend her workshops and consultancy to any designers, brands or retailers looking for expert industry advice on seamless knitwear design and education."
Clementine Hurley
Business Development Manager
Fashion & Product, ANZ
Australian Wool Innovation Limited
Clementine Hurley
Business Development Manager
Fashion & Product, ANZ
Australian Wool Innovation Limited
"We worked with Knovus on a design project developing a neck support for head drop for patients with ALS. We were developing a proof-of-concept for how a bespoke brace could be developed using digital fabrication technologies; creating 3D printed braces in hard plastic from 3D scan data. Ultimately we wanted to add a soft element to the brace while also exploring the fashion and expression element of this device that would be worn on the body. We approached KNOVUS due to their expertise in delivering 3D digital knit.
Although I am an experienced industrial designer, I have limited knowledge of soft goods design and development. Patricia was able to support us to evolve the soft goods element of the design from early concept to reality, as well as developing the proof of concept prototype through 3D knit. Supporting us from an early idea all the way to a finished product. Not only did we get a final result but, supported by Patricia, we learnt a lot about the soft goods and knitting along the way!"
Rowan Page
Senior Lecturer
ARC DECRA Fellow
Monash University
Rowan Page
Senior Lecturer
ARC DECRA Fellow
Monash University
"I embarked up on my technical knitting journey at Knovus, where Patricia took as through thoroughly planned introduction to knitting training modules. In a week I went from zero to hero, learning the basic fundamentals of technical knitting and whole garment programming.
The pace of education was excellent and tailored to each individual class member. I was happy to leave with detailed training manuals that continue to be a relevant resource to our whole garment knitting practice. I recommend Knovus as an excellent resource to begin or develop technical knitting knowledge for industry professionals."
Sacha Drake
Sacha Drake
Contact Us
90 Grattan Street
Carlton, VIC
Australia
knovus@knovus.com.au
+61 (03) 96121147
Carlton, VIC
Australia
knovus@knovus.com.au
+61 (03) 96121147
Company
Social
-
Facebook
-
Instagram
Copyright © 2025
Weft Knit
A method of knitting where yarns are fed into the machine horizontally—across the width of the fabric—to create a series of interlocking loops
A method of knitting where yarns are fed into the machine horizontally—across the width of the fabric—to create a series of interlocking loops
Warp Knit
Warp knitting is the formation of loops in a vertical direction using multiple strands of yarn, with each loop typically made from a separate thread and needle.
Warp knitting is the formation of loops in a vertical direction using multiple strands of yarn, with each loop typically made from a separate thread and needle.
Wale
Vertical columns of stitches in the lengthwise direction of the fabric.
Vertical columns of stitches in the lengthwise direction of the fabric.
Thermal bonding
A process where heat is applied to fuse thermoplastic fibres within a non-woven web, creating bonds at fibre intersections.
A process where heat is applied to fuse thermoplastic fibres within a non-woven web, creating bonds at fibre intersections.
Non-woven
Non-woven fabrics are created by bonding fibres together by various processes, such as mechanical, chemical, and thermal bonding
Non-woven fabrics are created by bonding fibres together by various processes, such as mechanical, chemical, and thermal bonding
Mechanical bonding
A process of creating non-woven fabrics by physically entangling fibres to hold them together.
A process of creating non-woven fabrics by physically entangling fibres to hold them together.
Knit
A textile produced by forming loops of yarn that are interlaced together, either across (weft knitting) or along the length of the fabric (warp knitting).
A textile produced by forming loops of yarn that are interlaced together, either across (weft knitting) or along the length of the fabric (warp knitting).
Flatbed knitting
Refers to the process or method of knitting using a flat, horizontal bed where yarn is fed in the weft direction to form fabric row by row.
Refers to the process or method of knitting using a flat, horizontal bed where yarn is fed in the weft direction to form fabric row by row.
Fibre
The basic raw material used to make yarns and fabrics. It refers to a fine, hair-like strand that can be natural or synthetic and is capable of being spun into thread or yarn.
The basic raw material used to make yarns and fabrics. It refers to a fine, hair-like strand that can be natural or synthetic and is capable of being spun into thread or yarn.
Courses
Horizontal rows of stitches that run widthwise across the knitted fabric
Horizontal rows of stitches that run widthwise across the knitted fabric
Circular knitting machine
Industrial circular-bed knitting machines that create tube-shaped pieces and are often used for larger and faster production. They are commonly used to produce finer knitwear.
Industrial circular-bed knitting machines that create tube-shaped pieces and are often used for larger and faster production. They are commonly used to produce finer knitwear.
Chemical bonding
A process in which fibres are joined together using adhesives or binders—such as resins or latex—that are applied to the fibre web and then cured, typically with heat, to create a stable, unified non-woven fabric structure.
A process in which fibres are joined together using adhesives or binders—such as resins or latex—that are applied to the fibre web and then cured, typically with heat, to create a stable, unified non-woven fabric structure.
Warp thread
The lengthwise yarns that run parallel to the selvedge of a woven textile.
The lengthwise yarns that run parallel to the selvedge of a woven textile.
Weft thread
The crosswise yarns that overlap and underlap the warp yarns are typically perpendicular to the selvedge in woven textiles.
The crosswise yarns that overlap and underlap the warp yarns are typically perpendicular to the selvedge in woven textiles.
Selvedge
The finished edge of a woven textile that runs along the lengthwise sides (parallel to the warp direction).
The finished edge of a woven textile that runs along the lengthwise sides (parallel to the warp direction).
Shima Seiki
A Japanese company founded in 1962, renowned for its advanced computerised flatbed knitting machines, most notably the WHOLEGARMENT® technology, which produces seamless knitwear.
A Japanese company founded in 1962, renowned for its advanced computerised flatbed knitting machines, most notably the WHOLEGARMENT® technology, which produces seamless knitwear.
Gauge
The number of needles per inch on a needle bed.
The number of needles per inch on a needle bed.
Intarsia
A knitting technique used to create patterns or images with distinct blocks of colour, where each area is knitted with a separate yarn source and yarns are not carried across the back, resulting in a flat, single-layered fabric.
A knitting technique used to create patterns or images with distinct blocks of colour, where each area is knitted with a separate yarn source and yarns are not carried across the back, resulting in a flat, single-layered fabric.
Multi-gauge
Knitting with a combination of needle combinations
Knitting with a combination of needle combinations
Complete garment knitting
Complete knitting also known as seamless, or 3D knitting refers to a method of producing complete knitted garments directly on the machine, eliminating or significantly reducing the need for post-knitting assembly such as cutting and sewing.
Complete knitting also known as seamless, or 3D knitting refers to a method of producing complete knitted garments directly on the machine, eliminating or significantly reducing the need for post-knitting assembly such as cutting and sewing.
Fully-fashioned
The shape of a garment piece is formed during knitting by increasing or decreasing stitches, rather than cutting fabric after knitting. This method allows for precise shaping (such as armholes, necklines, or sleeves) and produces pieces that require minimal trimming, resulting in a cleaner finish, less waste, and often a better fit.
The shape of a garment piece is formed during knitting by increasing or decreasing stitches, rather than cutting fabric after knitting. This method allows for precise shaping (such as armholes, necklines, or sleeves) and produces pieces that require minimal trimming, resulting in a cleaner finish, less waste, and often a better fit.
Jacquard
A knitting technique used to create multicolour patterns or motifs by selectively knitting different yarns across a fabric row. Unlike intarsia, jacquard patterns are made by carrying floats (unused yarns) across the back of the fabric, allowing for repeated designs and fine detail.
A knitting technique used to create multicolour patterns or motifs by selectively knitting different yarns across a fabric row. Unlike intarsia, jacquard patterns are made by carrying floats (unused yarns) across the back of the fabric, allowing for repeated designs and fine detail.
Knit programming
The process of creating machine-readable instructions that control computerised knitting machines to produce specific knit structures, patterns, and garments.
The process of creating machine-readable instructions that control computerised knitting machines to produce specific knit structures, patterns, and garments.
Technician
A skilled specialist responsible for the setup, adjustment, operation, and troubleshooting of knitting machinery.
A skilled specialist responsible for the setup, adjustment, operation, and troubleshooting of knitting machinery.
Manufacturer
The company or facility that produces knitted garments or fabric at scale. They manage the full process from programming and sampling to final production, often working with designers, brands, or developers.
The company or facility that produces knitted garments or fabric at scale. They manage the full process from programming and sampling to final production, often working with designers, brands, or developers.
Knit Programmer
A knit programmer is a specialist who translates a design into a machine-executable file using the compatible software for a specific type of knitting machine
A knit programmer is a specialist who translates a design into a machine-executable file using the compatible software for a specific type of knitting machine
Software
In knitting, software refers to the digital tools used to design, simulate, and program knitted fabrics or garments.
In knitting, software refers to the digital tools used to design, simulate, and program knitted fabrics or garments.
Production
The full process of manufacturing knit garments or fabric at scale, using programmed knitting machines. It begins after sampling and programming are finalised, and involves running machines continuously to produce finished pieces ready for linking, seaming, or finishing.
The full process of manufacturing knit garments or fabric at scale, using programmed knitting machines. It begins after sampling and programming are finalised, and involves running machines continuously to produce finished pieces ready for linking, seaming, or finishing.
Specification Sheet
A document that outlines all the technical details and requirements for a knitted product. It includes measurements, yarn types, stitch structures, construction notes, gauge, machine type, and finishing instructions used by manufacturers to ensure consistency and accuracy in production.
A document that outlines all the technical details and requirements for a knitted product. It includes measurements, yarn types, stitch structures, construction notes, gauge, machine type, and finishing instructions used by manufacturers to ensure consistency and accuracy in production.
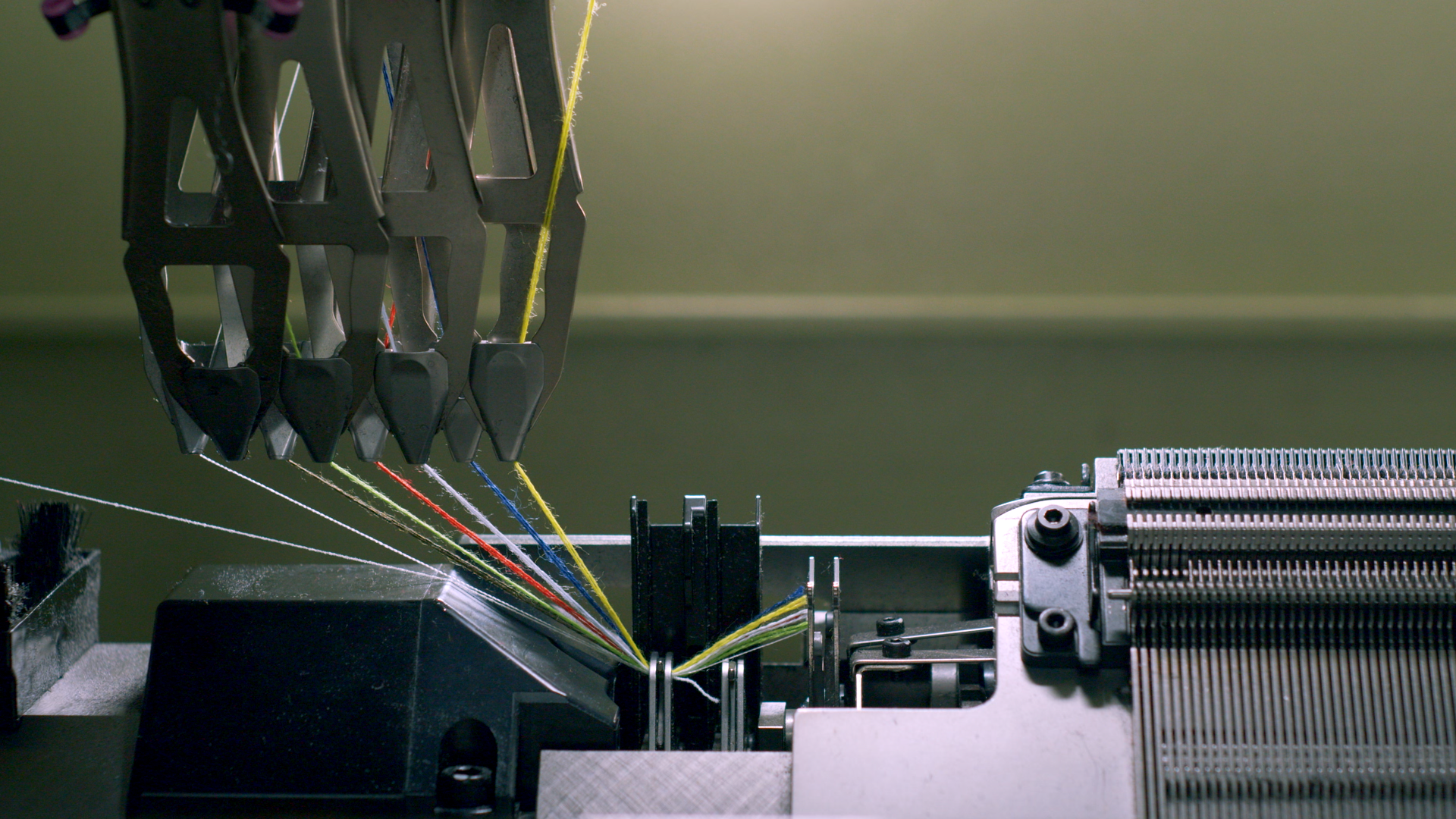
Yarn feeder/carrier
A moving component in a knitting machine that delivers yarn to the needles during the knitting process.
A moving component in a knitting machine that delivers yarn to the needles during the knitting process.
Needle bed
The needle bed is the component of a knitting machine that holds and guides the needles, allowing them to slide and create stitches.
The needle bed is the component of a knitting machine that holds and guides the needles, allowing them to slide and create stitches.
Stitch
The loop formed by the yarn during the knitting process.
The loop formed by the yarn during the knitting process.
Virtual Simulation
The process of using software (like Shima Seiki APEX) to digitally visualise a knitted fabric or garment.
The process of using software (like Shima Seiki APEX) to digitally visualise a knitted fabric or garment.
Product Development
The end-to-end process of turning a concept into a finished product. It includes design, material selection, programming, sampling, testing, and refining before full-scale production begins.
The end-to-end process of turning a concept into a finished product. It includes design, material selection, programming, sampling, testing, and refining before full-scale production begins.
Cut & Sew
A process where knitted fabric is produced in large panels and then cut and sewn together to create finished garments.
A process where knitted fabric is produced in large panels and then cut and sewn together to create finished garments.
Yarn Type
The material and structure of the yarn, including its fibre content (e.g. cotton, wool), thickness, twist, and whether it's spun or filament.
The material and structure of the yarn, including its fibre content (e.g. cotton, wool), thickness, twist, and whether it's spun or filament.
Tension
The size of the knitted loops and the takedown pressure applied during knitting.
The size of the knitted loops and the takedown pressure applied during knitting.
Speed
The rate at which the knitting machine operates.
The rate at which the knitting machine operates.
Take-down mechanism
This mechanism maintains fabric tension during knitting using roller systems or pull-down mechanisms.
This mechanism maintains fabric tension during knitting using roller systems or pull-down mechanisms.
Drape
The way a fabric hangs and flows when worn or handled.
The way a fabric hangs and flows when worn or handled.
Stitch density
The total number of loops in a measured area of fabric (such as a square inch or three square centimetres).
The total number of loops in a measured area of fabric (such as a square inch or three square centimetres).
Pattern resolution
The level of detail and clarity a knitted pattern can achieve is determined by the stitch size, gauge, and machine capability.
The level of detail and clarity a knitted pattern can achieve is determined by the stitch size, gauge, and machine capability.
Carriage
A movable component of a knitting machine that guides the yarn carrier across the needle bed to deliver yarn to the selected needles, producing the knitted fabric.
A movable component of a knitting machine that guides the yarn carrier across the needle bed to deliver yarn to the selected needles, producing the knitted fabric.
Machine gauge
The spacing of the needles on the needle bed (usually as needles per inch)
The spacing of the needles on the needle bed (usually as needles per inch)
Yarn Count
The yarn count number indicates the linear density (yarn diameter or fineness) to which that particular yarn has been spun
The yarn count number indicates the linear density (yarn diameter or fineness) to which that particular yarn has been spun
Stock service
A yarn stock service provides ready-to-shop yarns, often in a variety of colours, to customers.
A yarn stock service provides ready-to-shop yarns, often in a variety of colours, to customers.
Natural fibre
A fibre obtained from plants, animals, or minerals that can be spun into threads or yarns such as cotton, wool, silk, or flax.
A fibre obtained from plants, animals, or minerals that can be spun into threads or yarns such as cotton, wool, silk, or flax.
Synthetic fibre
A man-made fibre produced by polymerisation, a chemical process that combines small molecules into polymers; examples include polyester, nylon, and acrylic.
A man-made fibre produced by polymerisation, a chemical process that combines small molecules into polymers; examples include polyester, nylon, and acrylic.
Regenerated (semi-synthetic) fibre
A fibre derived from natural resources that has undergone an intensive chemical transformation process.
A fibre derived from natural resources that has undergone an intensive chemical transformation process.
Full gauge
Knitting with every needle.
Knitting with every needle.
Half gauge
Knitting with every second needle
Knitting with every second needle
The Direct System
The Direct System yarn count is the WEIGHT of a FIXED LENGTH of yarn (Weight per unit Length).
The Direct System yarn count is the WEIGHT of a FIXED LENGTH of yarn (Weight per unit Length).
The Indirect System
The LENGTH of a FIXED WEIGHT of yarn (Length per unit Weight).
The LENGTH of a FIXED WEIGHT of yarn (Length per unit Weight).
Numero metric (Nm)
Length in meters per 1 gram of mass.
Length in meters per 1 gram of mass.
Tex (tex)
Mass of yarn in grams per 1000 meters length.
Mass of yarn in grams per 1000 meters length.
Denier (den) fibre
Mass of yarn in grams for length of 9000 metres
Mass of yarn in grams for length of 9000 metres
Decitex (text)
Grams per 10,000 metres (10 kilometres)
Grams per 10,000 metres (10 kilometres)
English Cotton Count (ECC or Ne) fibre
Number of 840 yards of strands per 1 English pound of mass
Number of 840 yards of strands per 1 English pound of mass
Tech pack
The technical documentation that is created for garment or textile products. It contains flat sketches, material specifications, dimensions, instructions, and everything else the manufacturer needs to create products accurately.
The technical documentation that is created for garment or textile products. It contains flat sketches, material specifications, dimensions, instructions, and everything else the manufacturer needs to create products accurately.
Flatbed knitting machine
Industrial knitting machinery that has needle beds that sit flat, in a 'V' formation. The yarn passes across the needle bed horizontally.
Industrial knitting machinery that has needle beds that sit flat, in a 'V' formation. The yarn passes across the needle bed horizontally.
Microbial cellulose
A natural, biodegradable biopolymer synthesised by various bacteria.
A natural, biodegradable biopolymer synthesised by various bacteria.
Stitch Cams
A shaped mechanical component within the knitting machine’s cam system that controls how far needles move downward to form loops. It determines the loop length (stitch size), affecting fabric density and texture.
A shaped mechanical component within the knitting machine’s cam system that controls how far needles move downward to form loops. It determines the loop length (stitch size), affecting fabric density and texture.
System
A system refers to a complete yarn-feeding and needle-activating unit within the carriage that forms stitches independently during a knitting pass.
A system refers to a complete yarn-feeding and needle-activating unit within the carriage that forms stitches independently during a knitting pass.
Auto yarn feeders
A motorised yarn feeder that moves independently of the carriage, allowing yarn changes without requiring extra carriage passes.
A motorised yarn feeder that moves independently of the carriage, allowing yarn changes without requiring extra carriage passes.
Linker
A machine that joins knit panels stitch by stitch with high precision, producing fine seams and allowing edge-to-edge construction with excellent visibility and control.
A machine that joins knit panels stitch by stitch with high precision, producing fine seams and allowing edge-to-edge construction with excellent visibility and control.
Cup seamer
A machine that joins knit pieces using the knitting yarn and a secondary thread (typically cotton), producing strong seams quickly, where high precision is not required.